Description
Product Features High Reliability: Made of high-quality materials and using advanced manufacturing processes, it can meet the needs of various industrial applications and ensure stable operation in harsh environments. Easy Programming and Control: It supports multiple programming languages and communication interfaces, and can be conveniently connected to and controlled with devices such as PLCs and motion controllers. With an easy-to-use interface and fast processing speed, it can improve work efficiency. Strong Expandability: Its functions and performance can be expanded through expansion modules and function cards. With a high degree of customization, it can meet the special needs of different application scenarios. Diverse Functions: It can process various input signals such as digital signals and analog signals. It has functions such as the program capacity of the input module and an integrated IO processor, and can also achieve remote analog control. Efficient Computing Power: Equipped with a high-speed processor and a large-capacity memory, it can quickly execute complex control algorithms and data processing tasks, improving the system's response speed and operating efficiency. Modular Design: It is convenient for users to expand and upgrade, improving the flexibility and maintainability of the system and reducing maintenance costs. Easy Maintenance and Debugging: It has a self-diagnosis function, which can detect and report faults, making it easy for users to discover and solve problems in a timely manner. At the same time, it is convenient for debugging, allowing users to perform program debugging and system testing. Strong Compatibility: It is compatible with multiple CPU models and operating systems, and can be widely applied in different systems to meet the diverse needs of different users.
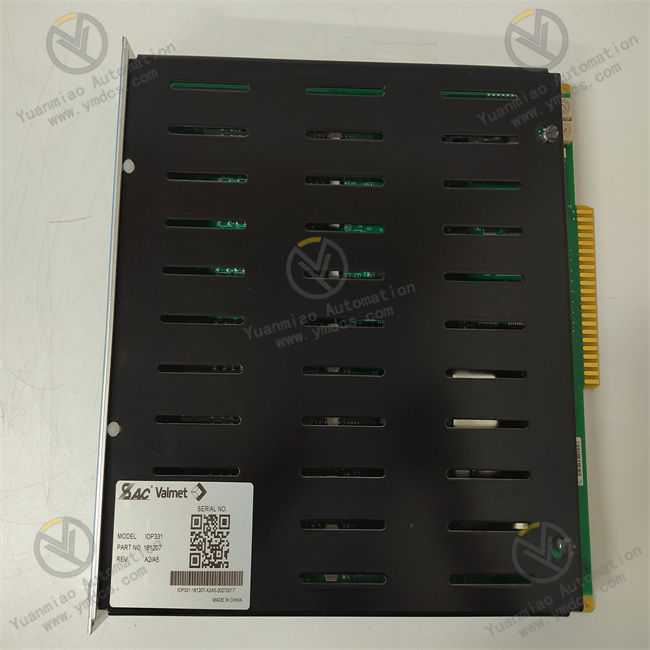

Application Scenarios
Industrial Automation: It is used to monitor, control, and coordinate various production processes. For example, in an automobile manufacturing production line, it can monitor signals such as the movements of robots and the positions of materials on the conveyor line, achieving the automation and efficient operation of the production process.
Process Control: In industries such as chemical engineering, petroleum, and pharmaceuticals, it can achieve complex process control, ensuring the stability of the production process and the consistency of product quality. For example, it can monitor parameters such as the temperature and pressure of chemical reaction kettles and control the feeding of materials and the reaction process.
Energy Industry: In the power system, it can be used to control and monitor the operation status of power equipment, collect signals from protection devices and measurement and control devices, and achieve fault diagnosis and the stable operation of the power system. In the water treatment process, it can control equipment such as water pumps and valves, monitor water quality parameters, and achieve the automated control of water treatment and the compliance of water quality.
Manufacturing Industry: Applied in production lines, it coordinates and controls mechanical equipment and technological processes, improving production efficiency and product quality. For example, in the production line of electronic devices, it controls the operation of equipment such as chip mounters and component inserters.
Cement and Mining Industry: It is used to control the ore processing and production process, such as controlling the operation of equipment like crushers and conveyor belts to achieve efficient ore mining and processing.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: In building automation systems, it can control refrigeration, air conditioning, and energy management systems, achieving a comfortable indoor environment in buildings and the rational use of energy. For example, it can automatically adjust the operation mode of the air conditioner according to the indoor temperature.
Transportation System: It plays a role in transportation-related applications such as traffic signal control and railway systems. For example, it controls the switching of traffic lights and realizes the automated control of railway turnouts.
General installation steps for common industrial control modules: Preparation Work Confirm the integrity of the equipment: Carefully inspect the appearance of the METSO IOP331 module to ensure there is no physical damage, missing components, etc. At the same time, confirm that all the equipped accessories (such as mounting rails, terminal blocks, fixing screws, etc.) are complete. Determine the installation location: Select a suitable installation location that meets the environmental requirements of the module, such as temperature, humidity, electromagnetic interference, and other conditions. Generally, it should be installed in a control cabinet that is dry, well-ventilated, and far away from strong electromagnetic field interference sources. Prepare installation tools: Get ready the tools required for installation, such as screwdrivers, wrenches, etc. Install the Mounting Rail If the rail mounting method (a common method) is adopted, first fix the mounting rail in a suitable position inside the control cabinet. Use a screwdriver or other appropriate tools to firmly install the rail on the cabinet body according to the mounting holes of the rail. Ensure that the rail is installed horizontally and firmly to avoid shaking during subsequent installation and use. Install the Module on the Rail Align the rail mounting buckle of the METSO IOP331 module with the mounting rail, and then gently snap the module onto the rail to ensure a tight fit between the module and the rail. During the snapping process, be careful not to use excessive force to avoid damaging the module or the rail. Electrical Connection Power connection: According to the power requirements of the module, use wires of appropriate specifications to connect to the power supply. Usually, a DC power supply (such as 24V DC) needs to be connected. Make sure to connect the power supply with the correct polarity to avoid damaging the module due to reverse connection. After connecting the power supply, tools such as a multimeter can be used to check whether the power voltage is normal. Input and output connection: According to the functions of the module and the actual application requirements, connect the input and output signal wires. For digital input signals, connect the corresponding sensors or switch devices; for output signals, connect them to devices such as actuators that need to be controlled. When connecting the signal wires, ensure that the wires are firmly connected to avoid unstable or interrupted signal transmission caused by looseness. At the same time, pay attention to the shielding and grounding of the signal wires to reduce electromagnetic interference. Communication connection (if applicable): If the module supports communication functions (such as Ethernet, serial communication, etc.), connect the communication cables according to the requirements of the communication interface. For example, if using Ethernet communication, connect the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet interface of the module and ensure that the network connection is normal. Fix the Module (if necessary) After completing the electrical connection, according to the installation requirements of the module, use fixing screws or other fixing devices to further fix the module on the rail to ensure that the module will not loosen during operation. Inspection and Testing Carefully check whether all installations and connections are correct to ensure there are no looseness, short circuits, or other errors. Check whether the insulation layer of the wires is damaged, whether the connection terminals are firm, etc. Switch on the power supply and observe the status of the indicator lights on the module. Under normal circumstances, the power indicator light should be on, and other indicator lights will have corresponding displays according to the working status and configuration of the module. If the indicator lights show abnormal conditions, refer to the fault diagnosis manual of the module for troubleshooting and resolution. Conduct simple functional tests, such as simulating input signals and observing whether the output of the module meets the expectations; sending commands through the communication interface to check whether the module can respond correctly, etc.

Main brands include: ABB, Bailey, GE, FOXBORO, Invensys TRICONEX, Bentley BENTLY, A-B Rockwell, EMERSON EMERSON, B&R, MOTOROLA, FUANC, REXROTH, KUKA, HONEYWELL, NI, DEIF, Yokogawa, WOODWARD WOODWARD, Ryan, SCHNEIDER SCHNEIDER, Yaskawa, MOOG, EPRO, PROSOFT and other major brands
Related Products
| VMIC VME7740-841 | SEW 31C075-503-4-00 |
| VMIC VMIPMC-5565 | SEW 31C450-503-4-00 |
| VMIC VMIVME-3122 | VIBRO 200-510-111-013 |
| VMIC VMIVME-7452 | VIBRO 200-560-101-015 |
| VMIC VMIVME7740-841 | VIBRO 200-566-101-012 |
| VMIC VMIVME-7750 | VIBRO 200-595-002-011 |
【 Disclaimer 】 We sell new products and discontinued products, independent channels to buy such special products. Guizhou Yuanmiao Automation Equipment Co., Ltd. is not an authorized distributor, dealer or representative of the products featured on this website. All product names/product images, trademarks, brands and microlabels used on this Website are the property of their respective owners. Descriptions, depictions or sales of products with such names/images, trademarks, brands and logos are for identification purposes only and do not imply any association or authorization with any rights holder.