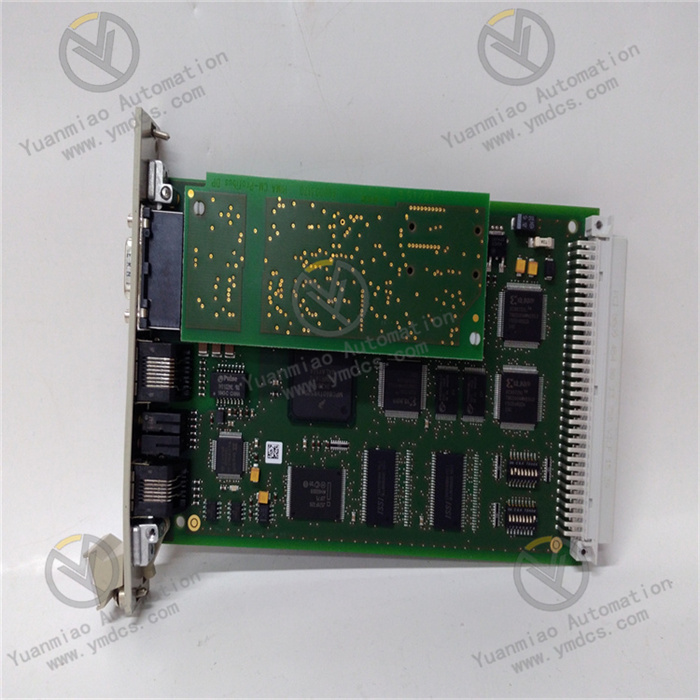
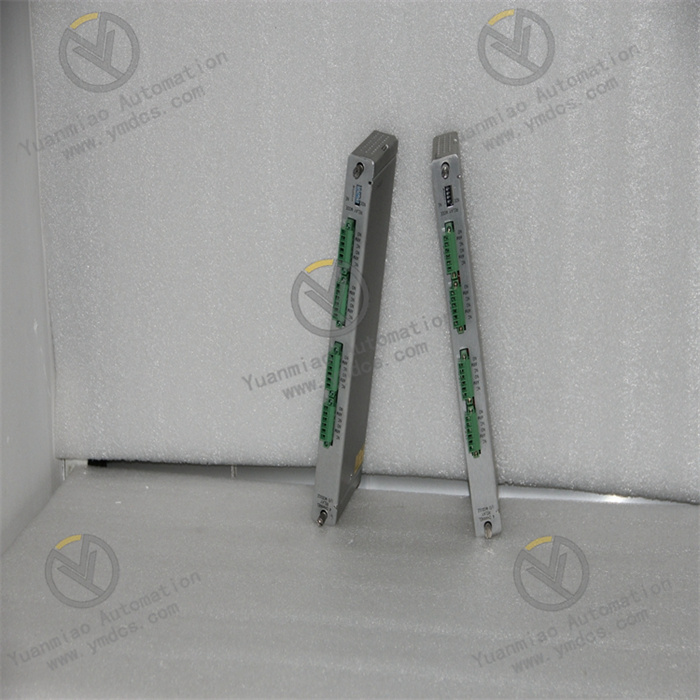
Description
General Information
- Product ID:HIEE200130R0002
- Catalog Description:AF C094 AE02 ARCnet control panel
- Country of Origin:Switzerland (CH)
- Frame Size:Undefined
- Gross Weight:0 kg
- Invoice Description:AF C094 AE02 ARCnet control panel
- Made To Order:No
- Minimum Order Quantity:1 piece
- Order Multiple:1 piece
- Package Level 1 Gross Weight:0 kg
- Package Level 1 Units:1 piece
- Part Type:New
- Product Net Depth / Length:285 mm
- Product Net Height:8 mm
- Product Net Weight:1.2 kg
- Product Net Width:21 mm

Working principle
Electromagnetic sucker controller: The AC voltage 380V is reduced by the transformer, rectified by the rectifier to 110V DC, and then entered into the sucker by the control device. At this time, the sucker is magnetized, and the reverse voltage line is entered during demagnetization, and the controller achieves the demagnetization function.
Access controller: The access controller works in two modes. One is the inspection mode, and the other is the recognition mode. In the inspection mode, the controller continuously sends the query code to the card reader and receives the reply command from the card reader. This pattern continues until the card reader senses the card. When the card reader senses the card, the card reader generates a different reply to the inspection command of the controller. In this reply command, the card reader transmits the code data of the sensor card to the access controller, so that the access controller enters the recognition mode. In the recognition mode of the access controller, the access controller analyzes the code in the sensor card, compares it with the card data stored in the device, and implements subsequent actions. After receiving data, the access controller sends a command to the card reader to restore the status of the card reader. At the same time, the access controller returns to inspection mode.
Combinatorial logic
The combinatorial logic controller consists of three parts: sequential circuit, instruction decoding circuit and combinatorial logic circuit. Through the instruction decoder to determine the current execution of the instruction, combined with the timing circuit generated by the beat, together as the combined logic circuit input results output the corresponding control signal. Combinatorial logic controller is composed of complex combinatorial logic gate circuit and flip-flop, which has high execution speed, so it is widely used in computer structures such as RISC.
Design steps:
1. Design the instruction system of the machine: specify the types of instructions, the number of instructions and the format and function of each instruction;
2. Preliminary overall design: such as register setting, bus arrangement, arithmetic design, connection relationship between components, etc.;
3, draw instruction flow chart: mark each instruction at what time, what part to perform what operation;
4, Arrange the operation schedule: that is, according to the instruction flow chart, decompose each operation into micro-operations, and list the micro-operations that the machine should carry out according to the time period;
5, list the microoperation signal expression, simplification, circuit implementation.
Basic composition:
1. The instruction register is used to store the instructions being executed. The instruction is divided into two parts: the operation code and the address code. The operation code is used to indicate the operation nature of the instruction, such as addition, subtraction, etc. The address code gives the operand address of this instruction or information about forming the operand address (in this case, the address formation circuit is used to form the operand address). There is an instruction called the transfer instruction, which is used to change the normal execution order of the instruction, the address code part of this instruction gives the address of the instruction to be forwarded to the execution.
2, the operation code decoder: used to decode the operation code of the instruction, generate the corresponding control level, and complete the function of a
There are two ways to do this:
The first method is to include the address of the next instruction in the instruction. The continuous operation of the program can be achieved by sending this address to the instruction address register during instruction execution. This method is suitable for early computers with serial devices such as magnetic drum and delay line as the main memory. According to the execution time of this instruction, the appropriate decision of the address of the next instruction can shorten the waiting time for reading the next instruction, and thus receive the effect of improving the program running speed.
The second option is to execute the instructions sequentially. A program consists of several program segments, the instructions of each program segment can be designed to be sequentially stored in the memory, so as long as the instruction address register has the function of counting, counting in the process of executing instructions, automatically adding an increment, you can form the address of the next instruction, so as to achieve the purpose of sequential execution of instructions. This method is suitable for computers with RAM as the main memory. When the running of the program needs to be transferred from one program segment to another, it can be realized by using the transfer instruction. The transfer instruction contains the address of the segment entry instruction to be transferred. When executing the transfer instruction, this address is sent to the program counter (at this time only as the instruction address register, not counting) as the address of the next instruction, so as to achieve the purpose of transferring the program segment. Subroutine calls, interrupts and traps are handled in a similar way. After the popularization of random access memory, the overall operation effect of the second method is greatly superior to the first method, so the sequential execution of instructions has become the method commonly used in mainstream computers, and the program counter has become an indispensable control component of the central processor.
Each function within the CPU performs a specific function. Information transfer between components and the realization of data flow control components. The path through which information is transmitted between many digital components is often referred to as a "data path." Where the information starts, through which register or multiplex switch in the middle, and finally to which register, must be controlled. The task of establishing a data path between registers is done by a component called the "operation controller".
The function of the operation controller is to generate various operation control signals according to the instruction operation code and the timing signal, so as to correctly establish the data path, so as to complete the control of obtaining instructions and executing instructions.
There are two kinds of controllers with different structures due to different design methods. Microoperations are non-decomposable operations that always require a corresponding control signal (called a microoperation control signal or microoperation command). A digital computer can be basically divided into two parts - the control part and the executive part. The controller is the control component, and the arithmetic device, memory, peripheral equipment is the executive component relative to the controller. A connection between the control unit and the executive unit is through the control line. The control component issues various control commands to the executive component through the control line. Usually, this control command is called a micro-command, and the operation performed by the executive component after accepting the micro-command is called a micro-operation. Another connection between the control unit and the executive unit is feedback information. The executive part reflects the operation situation to the control part through the feedback line, so that the control part can issue new micro-commands according to the state of the executive part, which is also called "state testing". Microoperations are a set of basic operations in an executive unit. Due to the structure of the data path, microoperations can be divided into
Compatibility and repulsion. In a CPU cycle of a machine, a group of microcommands that implement certain operational functions are combined to form a microinstruction. The general microinstruction format consists of operation control and sequence control. The operation control part is used to send out control signals to manage and direct the work of the whole aircraft. The sequence control part is used to determine the address to generate the next microinstruction. In fact, the function of a single machine instruction is realized by a sequence of many microinstructions. This sequence of microinstructions is often called a microprogram. Since microprograms are composed of microinstructions, when executing the cur

The company focuses on DCS, PLC, robot, large servo four systems
The main products are various modules/cards, controllers, touch screens, servo drivers
Company advantage: Supply imported original products, professional production of spare parts
One year warranty, fast delivery time, complete supply !!!
① 24 hours email response (12 hours);
② For shipment outside Asia, please contact the seller.
ABB Related Products
| 3HNA006580-001 | 3HNA012205-001 |
| 3HNA006581-001 | 3HNA012248-001 |
| 3HNA006582-001 | 3HNA012249-001 |
| 3HNA006583-001 | 3HNA012283-001 |
| 3HNA006584-001 | 3HNA012342-001 |
| 3HNA006585-001 | 3HNA012359-001 |
| 3HNA006586-001 | 3HNA012367-001 |
| 3HNA006605-001 | 3HNA012382-001 |
| 3HNA006650-001 | 3HNA012413-001 |
【 Disclaimer 】 We sell new products and discontinued products, independent channels to buy such special products. Guizhou Yuanmiao Automation Equipment Co., Ltd. is not an authorized distributor, dealer or representative of the products featured on this website. All product names/product images, trademarks, brands and microlabels used on this Website are the property of their respective owners. Descriptions, depictions or sales of products with such names/images, trademarks, brands and logos are for identification purposes only and do not imply any association or authorization with any rights holder. This article is from the official website of Guizhou Yuanmiao Automation Equipment Co., LTD. Please attach this link:http://www.ymdcs.com/ABB/














