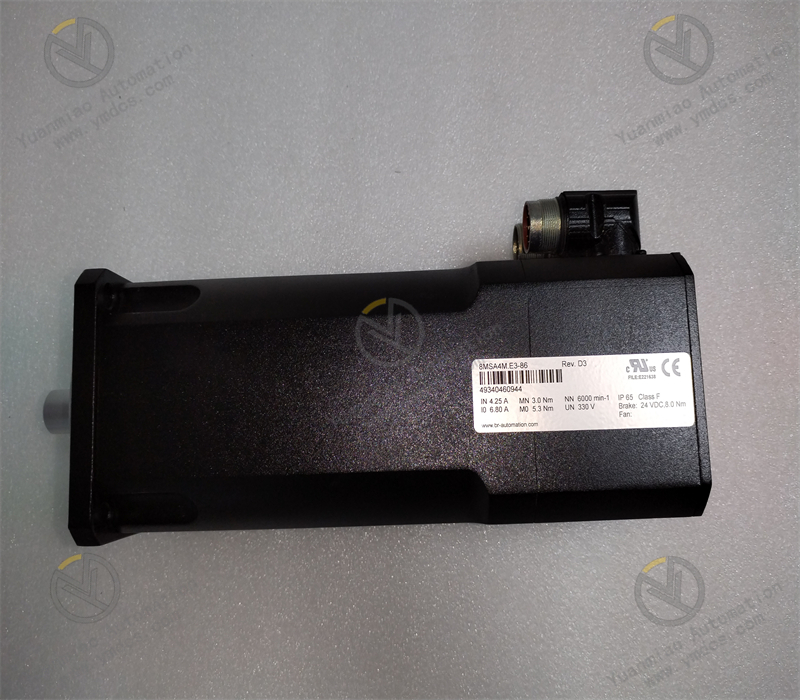
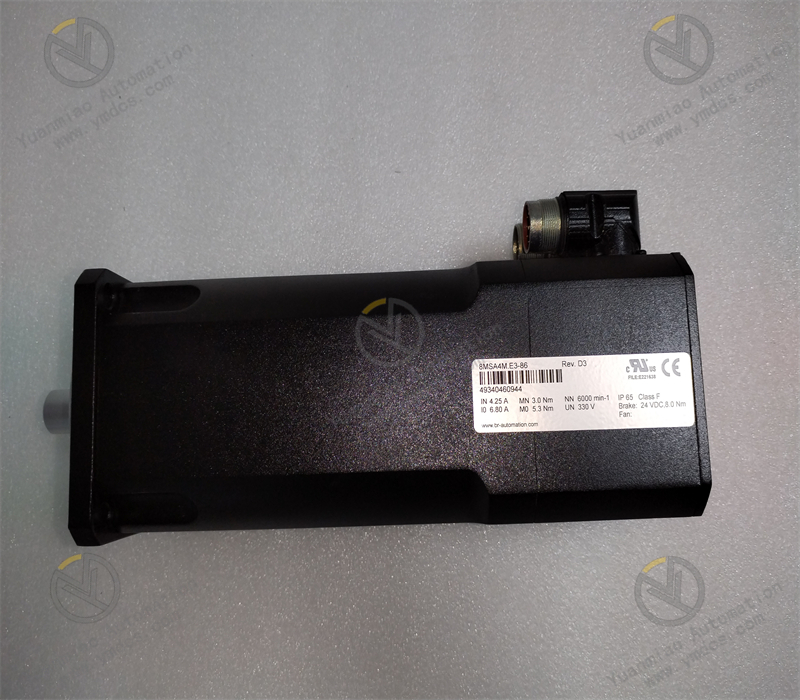
Description
Features: High overload capacity and peak torque: It can withstand large transient loads and performs excellently in situations where high power output is required for a short period of time. It can meet some application scenarios with high torque requirements. Long lifespan: Except for the bearings, almost all other components of the motor have no wear. This helps to reduce maintenance costs and extend the overall service life of the motor, making it suitable for industrial environments with long-term continuous operation. Complete motor system: Its stall torque ranges from 0.2N・m to 115N・m, providing a variety of torque specifications for selection to adapt to equipment with different load requirements.

Application fields:
Mechanical manufacturing: In equipment such as CNC machine tools and machining centers, it can provide precise position and speed control to ensure machining accuracy and efficiency.
Plastic processing: It is used in equipment such as injection molding machines and blow molding machines to achieve an efficient plastic molding process. It can precisely control parameters such as the opening and closing of the mold and the injection volume of plastic.
Textile and printing: In equipment such as textile machines and printing machines, it provides stable tension control and position synchronization to ensure the quality of textiles and the accuracy of printed patterns.
Packaging and logistics: In automated packaging lines and logistics conveying systems, it realizes rapid and accurate sorting and conveying of goods. It can control the speed of conveyor belts, the actions of robotic arms, etc.
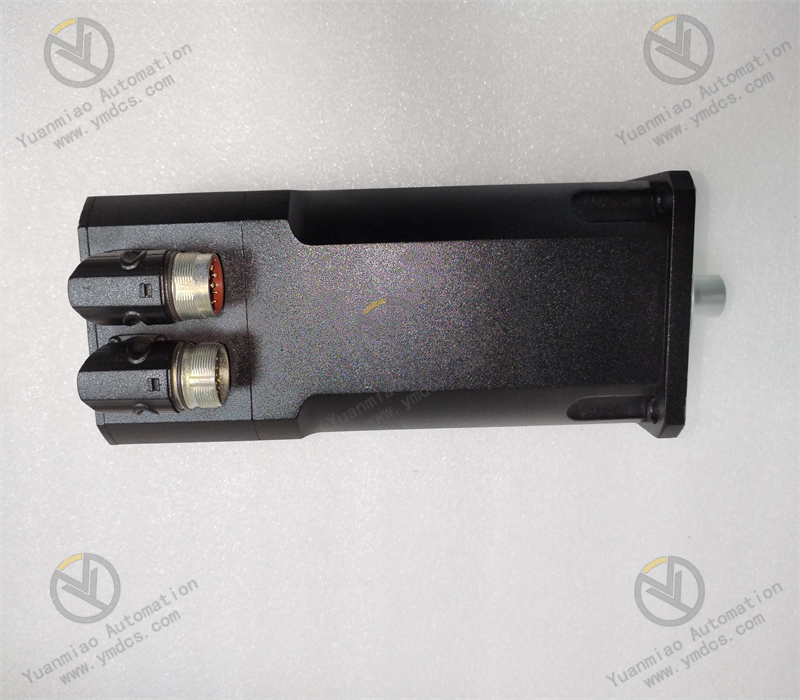

The working principle of the B&R 8MSA4M.E3-86 servo motor:
Electromagnetic Induction Drive Principle: The servo motor consists of two main parts, the stator and the rotor, inside. After a three-phase alternating current is applied to the stator winding, a rotating magnetic field will be generated. According to the principle of electromagnetic induction, the rotating magnetic field will induce an electromotive force and current in the rotor winding. The interaction between the rotor current and the rotating magnetic field generates an electromagnetic torque, which drives the rotor to rotate. In this way, electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy, enabling the motor to rotate.
Encoder Feedback Principle: In order to achieve precise position and speed control, the B&R 8MSA4M.E3-86 servo motor is equipped with an encoder. The encoder will monitor information such as the position, speed, and angle of the motor rotor in real time, and convert this information into electrical signals to be fed back to the servo driver. The driver compares the feedback signal with the input control signal and calculates the deviation value.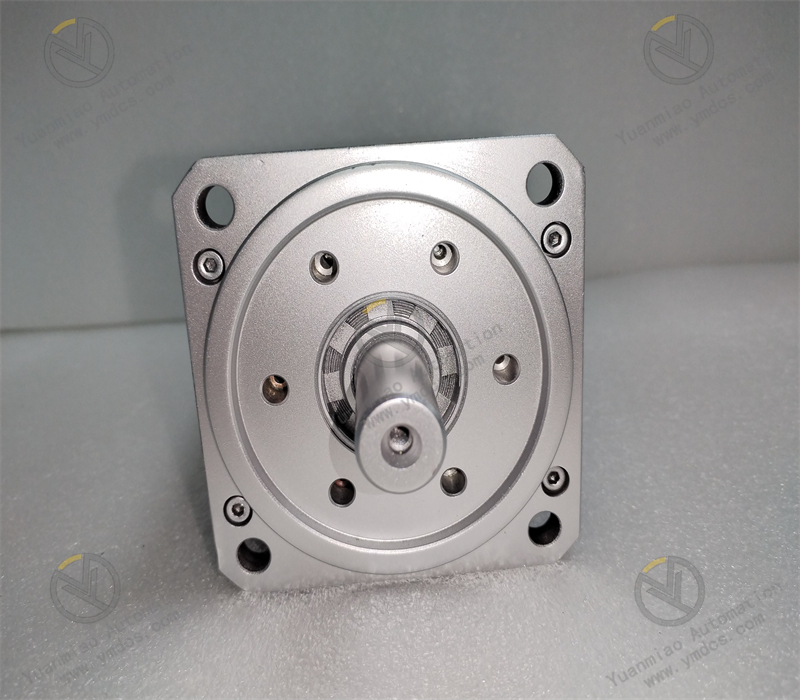 Servo Control Principle: The servo driver adjusts the magnitude and phase of the current and voltage output to the motor according to the deviation value, thereby changing the rotational speed and direction of the motor, making the actual operating state of the motor as close as possible to the target state. When the deviation value is zero, the motor reaches the target position or speed, achieving precise control. For example, in the position control mode, if the input position command signal changes and there is a deviation between the actual position of the motor and the target position, the encoder feeds back this deviation information to the driver. The driver adjusts the output to make the motor rotate until the motor reaches the target position and the deviation is eliminated.
Speed Control Principle: In the speed control mode, the servo driver receives the speed command signal and compares it with the actual speed signal fed back by the encoder. If the actual speed is inconsistent with the target speed, the driver will adjust the output current and voltage to change the electromagnetic torque of the motor, thereby adjusting the rotational speed of the motor to make it reach the target speed.
Torque Control Principle: In the torque control mode, the driver controls the magnitude of the current output to the motor according to the input torque command signal. Since the electromagnetic torque of the motor is proportional to the current, the torque output by the motor can be precisely controlled by controlling the current. This mode is often used in applications that require precise torque control, such as tension control and other situations.
Servo Control Principle: The servo driver adjusts the magnitude and phase of the current and voltage output to the motor according to the deviation value, thereby changing the rotational speed and direction of the motor, making the actual operating state of the motor as close as possible to the target state. When the deviation value is zero, the motor reaches the target position or speed, achieving precise control. For example, in the position control mode, if the input position command signal changes and there is a deviation between the actual position of the motor and the target position, the encoder feeds back this deviation information to the driver. The driver adjusts the output to make the motor rotate until the motor reaches the target position and the deviation is eliminated.
Speed Control Principle: In the speed control mode, the servo driver receives the speed command signal and compares it with the actual speed signal fed back by the encoder. If the actual speed is inconsistent with the target speed, the driver will adjust the output current and voltage to change the electromagnetic torque of the motor, thereby adjusting the rotational speed of the motor to make it reach the target speed.
Torque Control Principle: In the torque control mode, the driver controls the magnitude of the current output to the motor according to the input torque command signal. Since the electromagnetic torque of the motor is proportional to the current, the torque output by the motor can be precisely controlled by controlling the current. This mode is often used in applications that require precise torque control, such as tension control and other situations.

Main brands include: ABB, Bailey, GE, FOXBORO, Invensys TRICONEX, Bentley BENTLY, A-B Rockwell, EMERSON EMERSON, B&R, MOTOROLA, FUANC, REXROTH, KUKA, HONEYWELL, NI, DEIF, Yokogawa, WOODWARD WOODWARD, Ryan, SCHNEIDER SCHNEIDER, Yaskawa, MOOG, EPRO, PROSOFT and other major brands
【 Disclaimer 】 We sell new products and discontinued products, independent channels to buy such special products. Guizhou Yuanmiao Automation Equipment Co., Ltd. is not an authorized distributor, dealer or representative of the products featured on this website. All product names/product images, trademarks, brands and microlabels used on this Website are the property of their respective owners. Descriptions, depictions or sales of products with such names/images, trademarks, brands and logos are for identification purposes only and do not imply any association or authorization with any rights holder.