Description
Performance Characteristics: - High Efficiency and Reliability: By adopting advanced thyristor technology, it features high efficiency and reliability. This can ensure the stable operation of equipment, reduce the probability of failures, and lower the maintenance costs. - Good Controllability: It can precisely control the current, which in turn helps to optimize the performance of the equipment. It enables precise control of the motor speed and torque, improves energy efficiency, and saves operation costs. - Easy Maintenance: Equipped with self-diagnosis and fault protection functions, it can quickly locate faults and carry out maintenance, thus enhancing the availability and reliability of the equipment.
Common faults of the thyristor module: The module has no output. Causes of the fault: Power supply problem: The power supply is not properly connected, the power supply voltage is abnormal (too high or too low), or the power supply fuse is blown. Trigger circuit fault: The trigger signal is lost, or the components of the trigger circuit are damaged, resulting in the inability to trigger the thyristor to conduct. Thyristor damage: The thyristor itself is damaged due to reasons such as overcurrent, overvoltage, and overheating, and it cannot conduct normally. Solutions: Check the power supply: Use a multimeter to measure whether the power supply voltage is within the rated voltage range of the module. Check whether the power supply circuit connection is firm. Check whether the fuse is blown. If it is blown, replace the fuse with the same specification. Check the trigger circuit: Use an oscilloscope to detect whether the trigger signal is normal. Check whether components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes in the trigger circuit are damaged. If any are damaged, replace them. Test the thyristor: Use a professional semiconductor tester to test the conduction and cut-off characteristics of the thyristor to determine whether the thyristor is damaged. If it is damaged, replace the thyristor with the same model.
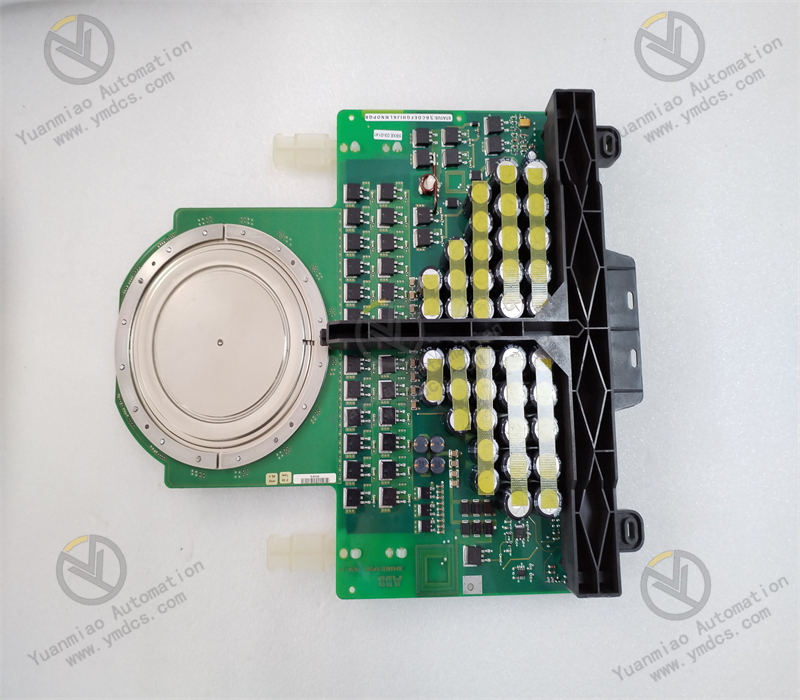

The module output is unstable.
Causes of the fault:
Load problem: The load is short-circuited, overloaded, or the load characteristics change, resulting in unstable module output.
Poor heat dissipation: The module's heat sink is blocked, the fan fails, or other reasons lead to the module's temperature being too high, affecting the performance of the thyristor.
Control signal interference: The control signal is interfered by external electromagnetic fields, resulting in an unstable trigger signal.
Solutions:
Check the load: Check whether there are short-circuit and overload situations in the load circuit. Measure whether parameters such as the resistance and current of the load are normal. If there are any abnormalities, eliminate the load faults.
Improve heat dissipation: Clean the dust on the heat sink. Check whether the fan is operating normally. Replace the fan if necessary to ensure good heat dissipation of the module.
Anti-interference treatment: Shield the control signal lines and add a filter circuit to reduce the impact of external electromagnetic interference on the control signal.
The module is overheated.
Causes of the fault:
Overload operation: The module is in an overloaded state for a long time, resulting in excessive power loss and generating too much heat.
Heat dissipation system failure: The heat sink has poor contact with the module, the cooling fan has insufficient speed, or the heat dissipation air duct is blocked, affecting the heat dissipation effect.
Internal component failure: Components such as resistors and capacitors inside the module are damaged, resulting in increased power loss and generating too much heat.
Solutions:
Adjust the load: Check whether the load exceeds the rated power of the module. If necessary, adjust the load size or replace the module with a higher power one.
Repair the heat dissipation system: Reinstall the heat sink to ensure good contact with the module. Clean the heat dissipation air duct. Check, repair, or replace the cooling fan.
Test the internal components: Use instruments such as a multimeter and an oscilloscope to test whether the parameters of the internal components of the module are normal. If any damaged components are found, replace them in a timely manner.

Main brands include: ABB, Bailey, GE, FOXBORO, Invensys TRICONEX, Bentley BENTLY, A-B Rockwell, EMERSON EMERSON, B&R, MOTOROLA, FUANC, REXROTH, KUKA, HONEYWELL, NI, DEIF, Yokogawa, WOODWARD WOODWARD, Ryan, SCHNEIDER SCHNEIDER, Yaskawa, MOOG, EPRO, PROSOFT and other major brands
[Disclaimer]
Guizhou Yuanmiao Automation Equipment Co., LTD. We sell new products and discontinued products, independent channels to purchase such special products. Guizhou Yuanmiao Automation Equipment Co., Ltd. is not an authorized distributor, distributor or representative of the featured products on this website. All product names/product images, trademarks, brands and logos used on this website are the property of their respective owners. Descriptions, descriptions or sales of products bearing these names, pictures, trademarks, brands and logos are for identification purposes only and do not imply any association or authorization with any rights holder.
This article is from the official website of Guizhou Yuanmiao Automation Equipment Co., LTD. Please attach this link: http://www.ymdcs.com/ABB